TheoryLongitudinal research suggests that genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors enhance one’s risk for developing Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias. According to our new Seed and Soil Model of Neurocognitive Disorders (McDonough & Allen, 2019), greater dementia risk might set the stage for a toxic brain environment that fosters such pathologic processes in high-risk brain regions. We hypothesized that candidate regions that would be most vulnerable would be those that have a high energy consumption and high interconnectivity with other brain regions, including the DMN and the medial temporal lobes.
|
Logo created by Jordan Puskas-Sullivan
|
Aims
- Test the notion that increased risk for dementia impacts the brain in convergent hub regions
- Identify novel risk factors for cognition and brain function
- Identify novel protective factors for cognition and brain function
Sample
- All participants were recruited from Tuscaloosa and Birmingham, Alabama
- 71 adults between the ages of 50 and 75
- 24 adults between 20 and 30 were recruited to serve as a comparison group
- Our initial dementia risk score was created using the presence of any of the following: subjective memory complaints, less than a high school education, African American or Hispanic ethnoracial category, mild head trauma, family history of AD, current diagnosis of hypertension or systolic blood pressure greater than 140 mmHg, current diagnosis or a family history of heart disease, current diagnosis of high total cholesterol, history or current use of smoking tobacco, current diagnosis or family history of diabetes, body mass index greater than 30 kg/m2, older than 65.
Neurocognitive Battery
Processing Speed: Digit Comparison, Trails A
Attention: ANT Alerting, ANT Orienting
Episodic Memory: Logical Memory, Verbal Paired Associates, Designs
Inductive Reasoning: Raven's Progressive Matrices
Executive Function: ANT Executive Attention, Trails B
Verbal Ability: WRAT Word Pronunciation, WRAT Sentence Completion
Global Cognition: St. Louis University Mental Status (SLUMS)
Everyday Function: Direct Assessment Functional Status (Communication Ability, Financial Ability, Medication Ability)
Attention: ANT Alerting, ANT Orienting
Episodic Memory: Logical Memory, Verbal Paired Associates, Designs
Inductive Reasoning: Raven's Progressive Matrices
Executive Function: ANT Executive Attention, Trails B
Verbal Ability: WRAT Word Pronunciation, WRAT Sentence Completion
Global Cognition: St. Louis University Mental Status (SLUMS)
Everyday Function: Direct Assessment Functional Status (Communication Ability, Financial Ability, Medication Ability)
Psychosocial and Health Survey
|
Emotion
|
Socio-Cultural
|
Health
|
Psychological
|
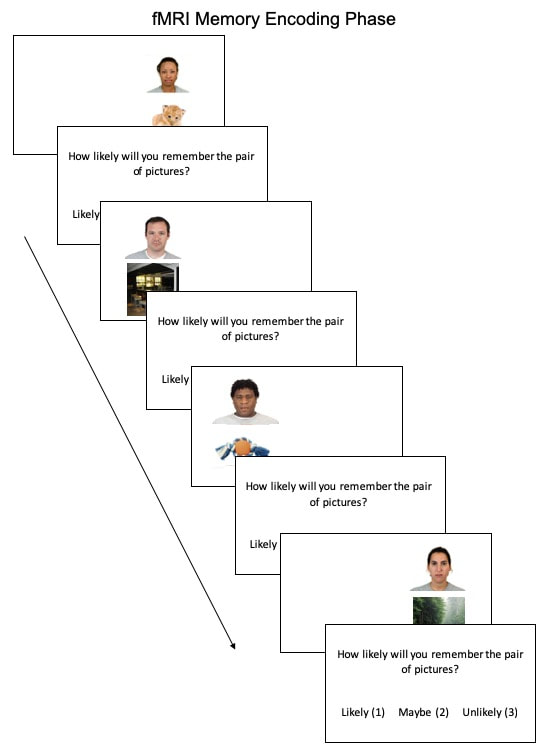
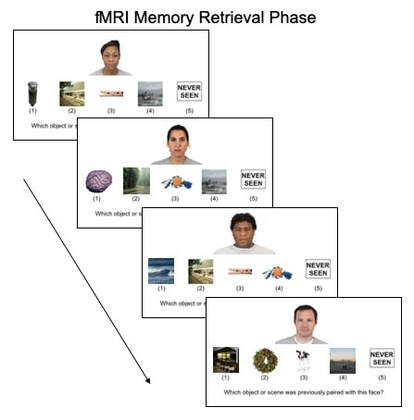
MRI
Resting State -> Encoding -> T1 M2PRAGE -> Resting State -> Retrieval -> Flashing Checkerboard
Publications from the Alabama Brain Study on Risk for Dementia
|
McDonough, I. M. & Madan, C. R. (2021). Structural Complexity is Negatively Associated with Brain Activity: A Novel Multimodal Test of Compensation Theories of Aging. Neurobiology of Aging, 98, 185-196.
Lin, S.-H. S. & McDonough, I. M. (2022). Intra-individual Cognitive Variability in Neuropsychological Assessment: A Sign of Neural Network Dysfunction. Aging, Neuropsychology, & Cognition.
|
Peak at the Data
Use our new Shiny App to take a peak at basic information from a subset of the variables: https://mac2research.shinyapps.io/shinyapp/
Access to the Data
|
Collaborative proposals are welcome! Please fill out the Study Proposal template and, if not affiliated with The University of Alabama, please also fill out the Individual Investigator Agreement. All forms should be sent to Dr. Ian McDonough at [email protected] with the Subject Line of the email titled, "ABSoRD Study Proposal Forms".
Once the specifics of the study are agreed upon, we will upload the Study Proposal to the Open Science Framework portal for pre-registration. |